- Waves is a word that we have commonly heard throughout our life ranging from the ones we see at the calm ocean to the invisible ones that move past us. However, what does a wave actually mean?
2. Waves are defined as travelling disturbances that function to transfer energy from a source to
the surroundings. ( Note : Waves transfer energy and not particles!)3. Now, a little deeper, you should know that 2 types of waves exist in our world which can be
divided into:
a) transvese waves
- Waves in which the particles of the wave vibrate perpendicular to the direction of
propogation.

Sea waves are an example of a transverse waves
b) longitudinal waves
- Waves in which the particles of the wave vibrate parallel to the direction of
propogation


Sound waves are a type of longitudinal waves
4. Differences in the waves

THE COMPONENTS OF A WAVE

Wave diagram
1. Amplitude - Maximum displacement of the wave particle
2. Period(T) - The time taken for one complete oscillation
3. Frequency(f) - The number of oscillations completed in 1 sec
4. Displacement(s) - Distance of the wave particle from the equilibrium position
OSCILLATING SYSTEMS
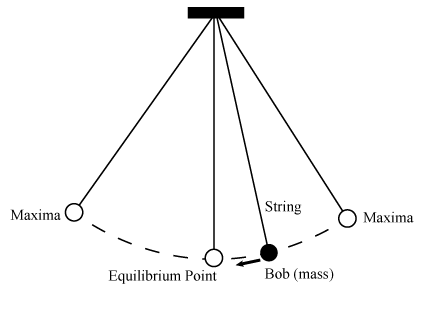 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OSCILLATION OF A SIMPLE PENDULUM BOB |
2. Related formula :
a) Period of oscillation - 2Л√(l/g)
b) l = length of pendulum
g = acceleration due to gravity
mass does not affect the equation
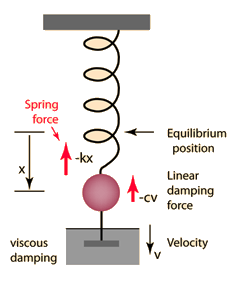
3. Related formula : a) Period of oscillation- 2Л√(m/k)
m - mass of the load
k - spring constant
WAVELENGTH( 𝛌)
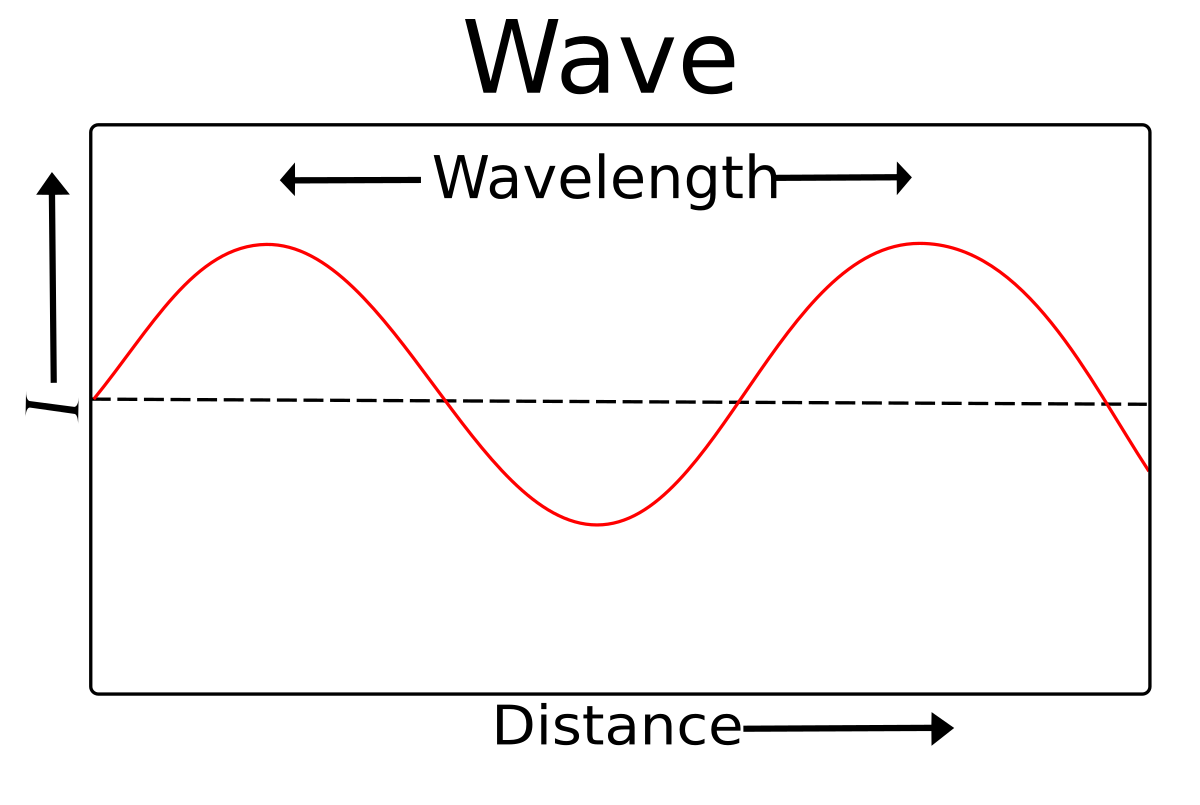
1. The distance between 2 successive points which has the same phase
2. Two points in the same phase have same displacement and direction of vibration
of vibration are the same phase.
3. The distance between 2 successive crests or troughs.
4. The speed of the wave is the distance travelled by the wave per unit time.
5. Frequency of a wave is the number of cycles completed per second.
IMPORTANT FORMULAS THROUGHOUT THE TOPIC
1. Period , T = 1/F or F = 1/T ( F = frequency, T = period)
2. Wave formula :
a) v = f𝛌
- v = speed of the wave
- f = frequency of the wave
- 𝛌 = wavelength
PHENOMENON INVOLVING WAVES
1. Reflection

2. Refraction

3. Diffraction
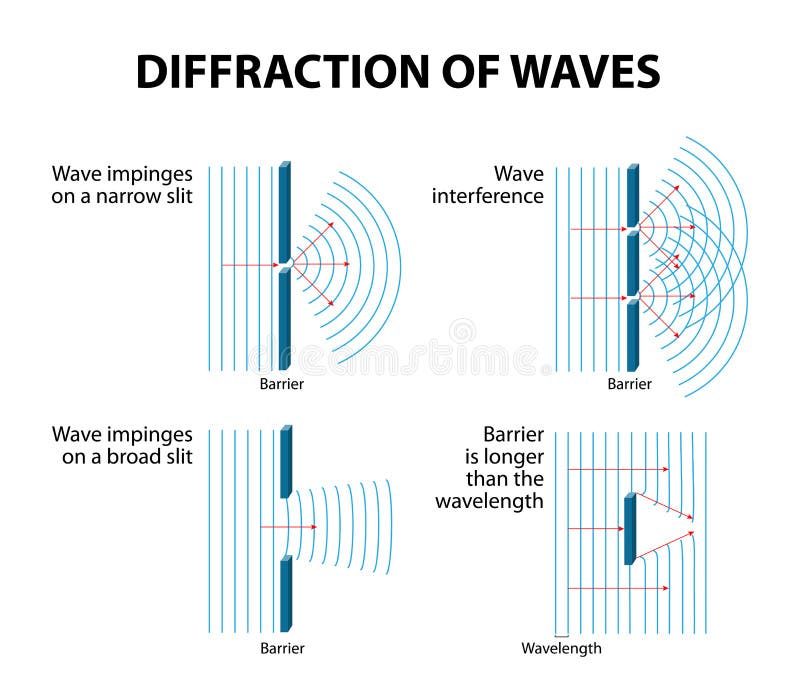
4. Interference

Conclusion : If you would like to know more about waves , please take a look at this video clip here
. That's all from me. Bye!

No comments:
Post a Comment